Enterprise-level network equipment on the secondary market hide sensitive data that hackers could use to breach corporate environments or to obtain customer information.
Looking at several used corporate-grade routers, researchers found that most of them had been improperly wiped during the decommissioning process and then sold online.
Core routers for sale
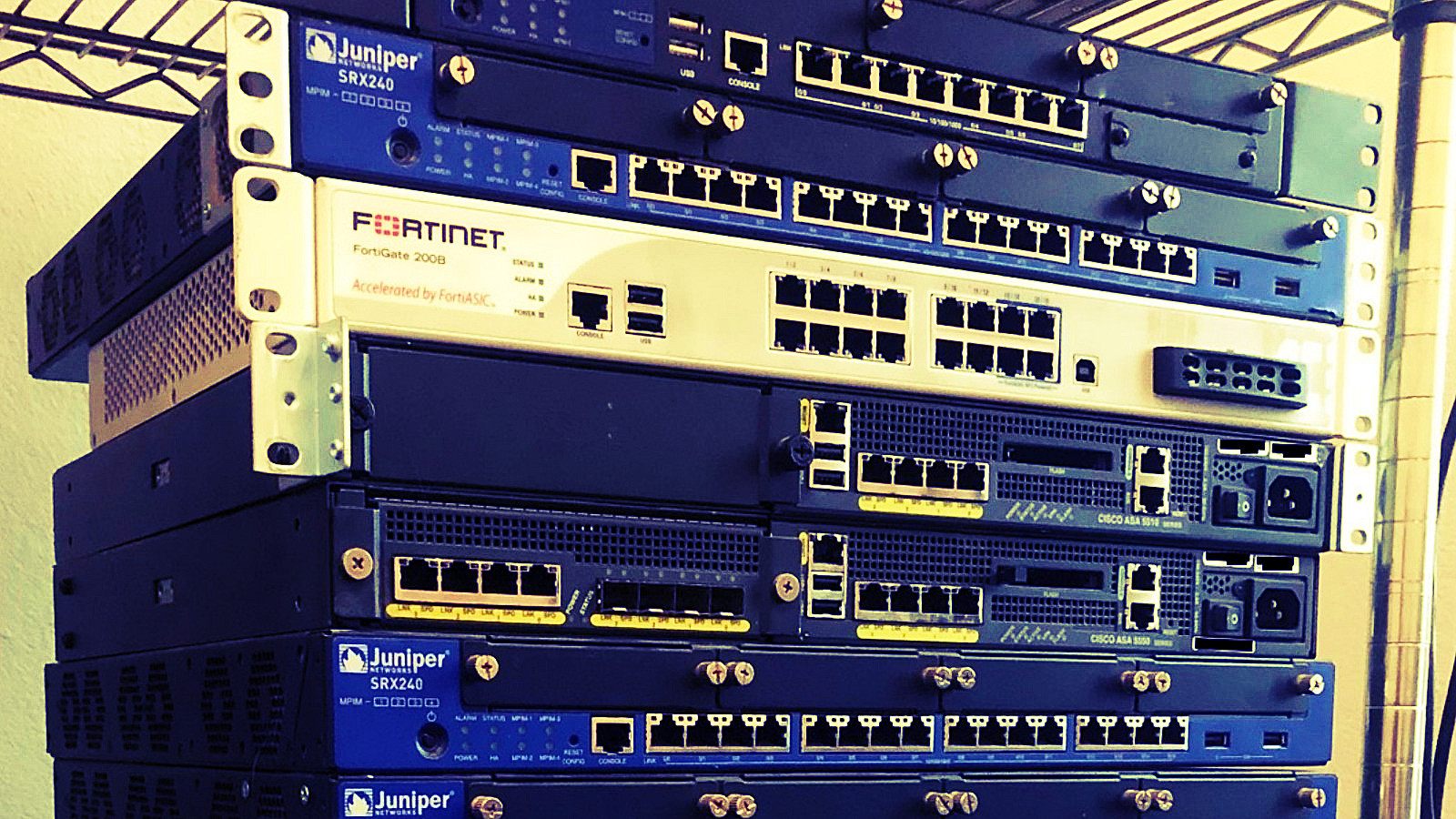
Researchers at cybersecurity company ESET purchased 18 used core routers and found that the full configuration data could still be accessed on more than half of those that worked properly.
Core routers are the backbone of a large network as they connect all other network devices. They support multiple data communication interfaces and are designed to forward IP packets at the highest speeds.
Initially, the ESET research team bought a few used routers to set up a test environment and found they had not been properly wiped and contained network configuration data as well as information that helped identify the previous owners.
The purchased equipment included four devices from Cisco (ASA 5500), three from Fortinet (Fortigate series), and 11 from Juniper Networks (SRX Series Services Gateway).
In a report earlier this week, Cameron Camp and Tony Anscombe say that one device was dead on arrival and eliminated from the tests and two of them were a mirror of each other and counted as one in the evaluation results.
Of the remaining 16 devices, only five were properly wiped and just two had been hardened, making some of the data more difficult to access.
For most of them, though, it was possible to access the complete configuration data, which is a trove of details about the owner, how they set up the network, and the connections between other systems.
With corporate network devices, the administrator needs to run a few commands to securely wipe the configuration and reset it. Without this, the routers can be booted into a recovery mode that allows checking how it was set up.
Secrets in the network
The researchers say that some of the routers retained customer information, data that allowed third-party connections to the network, and even “credentials for connecting to other networks as a trusted party.”
Additionally, eight of the nine routers that exposed the full configuration data also contained router-to-router authentication keys and hashes.
The list of corporate secrets extended to complete maps of sensitive applications hosted locally or in the cloud. Some examples include Microsoft Exchange, Salesforce, SharePoint, Spiceworks, VMware Horizon, and SQL.
“Due to the granularity of the applications and the specific versions used in some cases, known exploits could be deployed across the network topology that an attacker would already have mapped” - ESET
Such extensive insider details are typically reserved for “highly credentialed personnel” such as network administrators and their managers, the researchers explain.
An adversary with access to this type of information could easily come up with a plan for an attack path that would take them deep inside the network undetected.
“With this level of detail, impersonating network or internal hosts would be far simpler for an attacker, especially since the devices often contain VPN credentials or other easily cracked authentication tokens” - ESET
Based on the details uncovered in the routers, several of them had been in environments of managed IT providers, who operate the networks of large companies.
One device even belonged to a managed security services provider (MSSP) that handled networks for hundreds of clients in various sectors (e.g. education, finance, healthcare, manufacturing).
Following their findings, the researchers highlight the importance of properly wiping network devices before getting rid of them. Companies should have procedures in place for the secure destruction and disposal of their digital equipment.
The researchers also warn that using a third–party service for this activity may not always be a good idea. After notifying the owner of a router of their findings, they learned that the company had used such a service. “That clearly didn’t go as planned.”
The advice here is to follow the recommendations from the device maker to clean the equipment of potentially sensitive data and bring it to a factory default state.


Comments
mikebutash - 10 months ago
As a common purchaser or aftermarket gear for my lab, it's literally every time I get a device that is still running the last company's configuration. These "e-recyclers" are obviously not doing their jobs correctly and with no oversight. I know some, they're junk dealers, not network and security engineers.
Cisco kit is always funny, because silly admins never secure them properly, so I rommon them, restore the config into admin, and parse it for all the insecurely configured type-7 passwords just to see what they were using. Commonly weak passwords of course. Almost all even if not getting passwords I get the rest of their configurations, whether cisco, arista, extreme, juniper, whatever.
The last Fortigate I've used for 4 years I purchased on ebay, after a quick break-in and factory reset, getting into it I found it phoned home and rejoined the old company support, which was still active with full Enterprise support for another year. Score for my lab! That year went by, and to my shock, my support renewed with the company again.. and again, a total of 4 years I used that until it went end of support/life.
The moral of the forigate story was I looked up the company when I got it and they were a US Defense contractor, I presume too rich to care about some random device sent to e-recycling, or care not for the $1500 support they were paying each year for it still. Nor for who knows how many others like it they recycled off at the time.
In all cases, I could probably be far worse about what I do when I do harvest creds off old devices, but lucky for them I stay on the white-hat end of things. Certainly others do not.
h_b_s - 10 months ago
This happens with hard drives from contract recyclers as well. It's well known in the hacker community that if you want to get into a network, just grab the owner's discarded hardware from the trash bin. It's likely impossible to know how many corporate compromises began with a dumpster dive or e'bay purchase, but I doubt it's 0.
This is a process that should likely never be outsourced, because there's no regulation on that industry, but nearly always is because of money. Apparently no one asks why those services are so comparatively cheap.