How to use the Windows 8 System Recovery Environment Command Prompt
Lawrence Abrams
- October 24, 2012
- Read 503,430 times
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How to start the Recovery Environment Command Prompt in Windows 8
- List of Windows 8 Recovery Environment Command Prompt commands
- How to load a registry hive in the Recovery Environment Command Prompt
- How to determine the drive letter of your Windows drive
- Conclusion
When Windows is no longer able to start it is typically because of a problem in the Windows Registry, a driver conflict, or malware crashing the computer. Windows startup issues can be one of the most frustrating issues to deal with because you do not have easy access to the file and data we need to fix these problems. Thankfully, we can use the Windows 8 Recovery Environment Command Prompt to assist us in resolving these types of problems. This tool allows you to access your Windows Registry and file system when Windows is offline. This will allow you to fix numerous issues such as corrupt Registry data and malware infections.
The Recovery command prompt is especially useful when it comes to removing Rootkits. One of the biggest trends in computer infections is the use of rootkits that hide files and Registry information while they are running in Windows. By using the Recovery Command Prompt you will have full visibility into the files that these rootkits are hiding or using because Windows, and the malware, will not be started. This allows you to quickly find the infections and remove them so that they are not active the next time you start Windows.
This tutorial will explain how to access the Recovery Command Prompt and use it efficiently. We have also outlined how you can access your offline Registry and some basic commands to help you get started using this powerful tool.
How to start the Recovery Environment Command Prompt in Windows 8
To access the Command Prompt in the Windows Recovery Environment you need to go to the Windows 8 Start Screen and type Advanced. When the search results appear click on the Settings category as shown below.
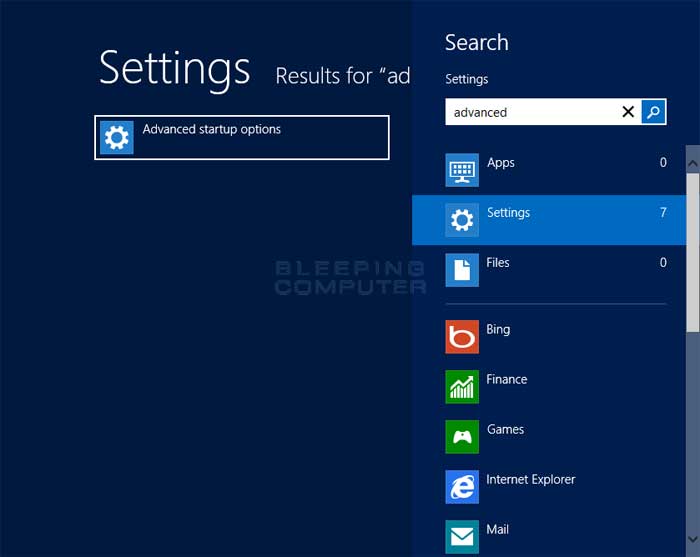
Now click on the option labeled Advanced startup options and you will be brought to the General PC Settings screen. Scroll down to the bottom until you see an option labeled Advanced startup.
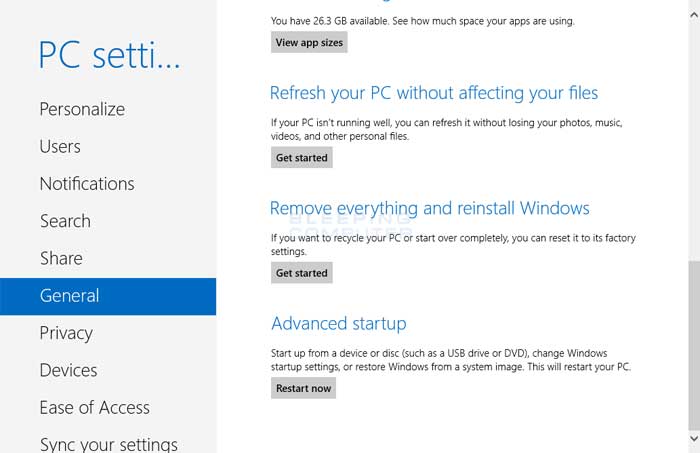
Click on the Restart now button and Windows 8 will restart your computer and go directly into the Advanced Startup options menu.
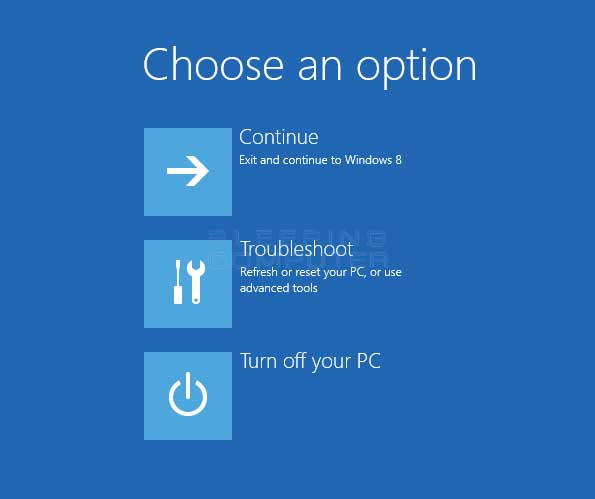
Now click on the Troubleshoot button and then the Advanced options button. When the advanced options screen opens, click on the Command Prompt option. A new screen will be displayed with an open command prompt.
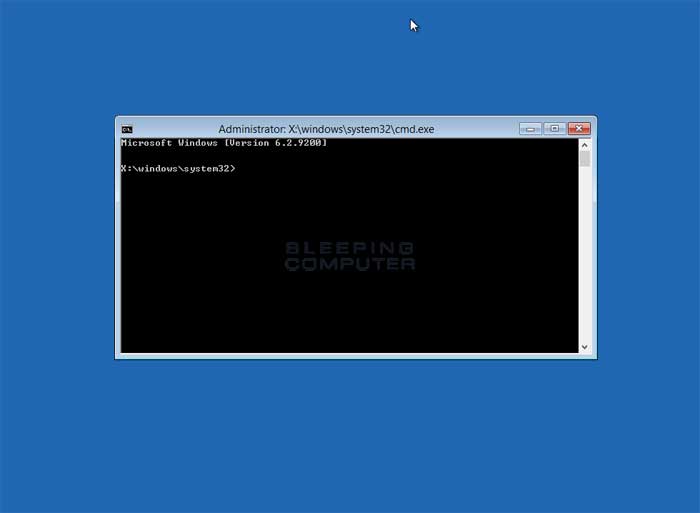
The Company Prompt is a small black Windows that displays your current folder location on the computer. To use the Command Prompt, you need to type in commands that you wish your computer to execute. A list of the commands that you can use in the Recovery Environment Command Prompt can be found in the next section. When you are done using the command prompt, you should type Exit to get back to the Advanced options menu, where you can reboot your computer.
List of Windows 8 Recovery Environment Command Prompt commands
Unlike Windows, which has a graphical user interface, the Windows 8 Recovery command prompt requires you to type in all your commands. Simply type a valid command that you wish to perform and then press the Enter key on your keyboard. It is also possible to start some graphical programs like Notepad or an antivirus program from within the Recovery Console command prompt. Unfortunately, not every Windows program will run in this environment, so you will need to test each one to determine if they will work.
A partial list of commands and prompts that work within the command prompt are listed below. To get help on how to use these commands, you can use the /h or /? arguments to get help information for the commands. For example, if you wish to see the help information for bcdedit you would type bcdedit /h and then press Enter on your keyboard. The help information for the program would then be displayed in the command prompt. If there is too much information, you can pipe the help information through the more command. This allows you to see the help information one page at a time. To do that you would type bcdedit /h | more and press Enter on your keyboard.
The list of commands are:
|
Console Command
|
Description
|
| attrib | Allows you to change permissions on files. |
| bcdboot | BCDboot is a tool used to quickly set up a system partition, or to repair the boot environment located on the system partition. |
| bcdedit | Displays and allows you to change how Windows boots up. This command is useful for people who are having trouble with the Windows Boot Manager |
| cd | Changes the current directory to another directory. |
| chkdsk | Checks a hard disk for errors and attempts to repair them. |
| copy | Copy a file from one location to another. |
| defrag | Allows you to defrag your hard drive. |
| del | Deletes a file |
| dir | Lists the files and folders in the current directory |
| diskpart | Load the Windows disk management program. From this program you can create, delete, shrink, and expand your existing partitions as well as get information about partitions and hard drives |
| format | Allows you to format drives. |
| icacls | Change file and folder permissions and display or modify access control lists (ACLs) |
| manage-bde.exe | Configure BitLocker drive encryption on disk volumes. |
| mkdir | Creates a new folder |
| more | Displays the content of a file one page at a time |
| move | Moves a file or a folder |
| recover | Allows you to attempt to recover files from a damaged drive. |
| reg | Perform Windows Registry operations. |
| ren | Rename a file or folder |
| rd | Remove an empty folder |
| sfc | Scans and checks the integrity of your Windows files. Useful way to see if a system file is missing or has been tampered with. |
| type | Display the contents of a file |
| xcopy | Copy a folder or files to another location |
|
Windows Program Name
|
Description/Notes
|
| bmrui.exe | This command will open the System Image Recovery screen to restore Windows from an image. |
| Notepad.exe | Opens up the Windows Notepad so you can view and edit text files. You can also use the file browser when click the File -> Open menus to copy, move, rename, and delete files. |
| Regedit.exe | The Windows Registry Editor. |
| rstrui.exe | The System Restore console where you can restore your computer back to earlier restore points. |
When you are finished using the Command Prompt you can exit it by typing exit and then pressing the Enter key on your keyboard. The command prompt will close and you will now be back at the list of available repair tools, where you can reboot your computer.
How to load a registry hive in the Recovery Environment Command Prompt
An extremely important feature of the Recovery Command Prompt is the ability to load Windows Registry hives and then be able to access them with Regedit. This will allow you to stop computer infections from automatically starting or repair corrupt Registry data that may be causing issues when starting Windows 8. A good example of how this can be used is when a computer infection is locking your desktop when you start Windows. To fix this, you would just start the Windows Recovery Environment Command Prompt, load the hives, delete the Run value that is loading the infection, and unload them again. Then when you restart your computer the infection will not be started and you can access your desktop again.
A registry hive can be loaded using the reg command. For more information on how to use this command, you can type reg load /? and press Enter on your keyboard. An example of how we can load Registry hives to fix a corrupt Userinit entry can be seen below:
Type REG LOAD HKLM\WinSoft
:\Windows\System32\config\software and press Enter to load the HKLM\Software Registry hive as the WinSoft key.Type regedit.exe and press Enter to start the Windows Registry Editor. When the Registry editor is started, browse to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run key.
Look for the Registry value that is loading the computer infection and delete it.
Close the Windows Registry Editor.
In the command prompt type REG UNLOAD HKLM\WinSoft and press Enter to unload the Registry hive.
Type exit and press Enter on your keyboard to go back to the Advanced Options screen. You can then reboot your computer from there.
Please note that in the above commands I have specified drive letters as
How to determine the drive letter of your Windows drive
When you are in the Recovery Command Prompt, the drive letters for your hard drives changes. This can cause your Windows install to be listed under a different drive letter than it normally has. To find out the drive letter assigned to your normal Windows drive, you can use the bcdedit.exe program.
To find the drive letter of your Windows installation under the Recovery Command Prompt, please type the following command and then press Enter on your keyboard.
bcdedit | find "osdevice"
When you run this command it will display output that is similar to os device partition=D:. The letter after the partition= is the drive where Windows installation resides. To change your current working directory to that drive, you can type D:, or whatever other drive letter it shows, and press Enter on your keyboard.
As you can see the Windows 8 Recovery Command Prompt is a powerful tool for fixing problems that would normally not allow you to start Windows. The ability to access your files and the Windows Registry while Windows 8 is offline is a powerful tool for fixing corrupted Registry and removing malware. If you find other useful programs or tools for the Windows Recovery environment please let us know in the forums so we can update this tutorial.
As always if you have any questions or tips on using the Windows 8 Recovery Environment command prompt you should let us know in the Windows 8 Forum.






